Choosing the right web hosting is critical for online success. This comprehensive guide explains what a Virtual Private Server (VPS) is, how it works, and its advantages and disadvantages. We’ll compare VPS hosting to shared hosting, dedicated servers, and cloud hosting, helping you determine if a VPS is right for you. We also cover key criteria for choosing a VPS provider and answer frequently asked questions, providing a complete resource for understanding VPS hosting. This will benefit anyone considering changing their hosting environment.
What is VPS?
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a virtual machine sold as a service by web hosting providers. It uses virtualization technology to divide a physical server into multiple, isolated virtual servers, each with dedicated resources and its own operating system.
A VPS is like having your own apartment within a larger building. You have your own dedicated space and resources, but you still share the underlying infrastructure (the building itself) with other tenants. A dedicated server, in contrast, would be like owning an entire house.

How Does a VPS Work?
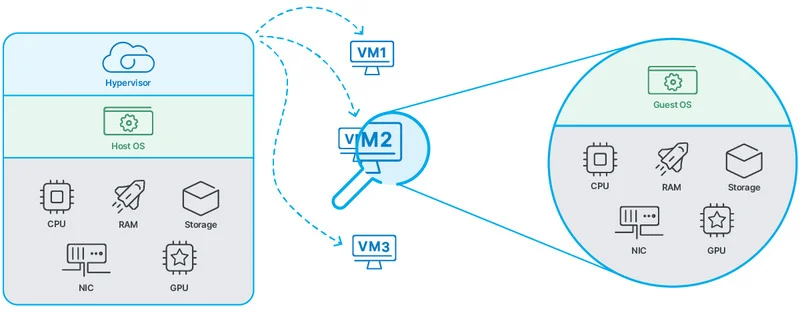
A VPS works by using virtualization technology to divide a single physical server into multiple, isolated virtual servers. Each of these virtual servers acts like an independent, dedicated server, despite sharing the same physical hardware.
The key component that makes this all possible is called a hypervisor. Think of the hypervisor as a very sophisticated resource manager. It’s a software layer that sits directly on the physical server’s hardware (this is often referred to as a “bare-metal” hypervisor). It’s responsible for creating, running, and managing the virtual machines. Popular hypervisors include KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine), Xen, and VMware ESXi.
When a physical server is set up for VPS hosting, the hypervisor divides the server’s resources – CPU, RAM, storage, and network bandwidth – and allocates a specific portion to each virtual machine. This allocation is crucial. It ensures that each VPS has the resources it needs to operate smoothly and independently. For example, one VPS might be allocated 2 CPU cores, 4GB of RAM, and 80GB of storage, while another on the same physical server might have 4 CPU cores, 8GB of RAM, and 160GB of storage.
Because each VPS has its own dedicated resources, it also runs its own separate operating system (OS). This is another crucial difference from shared hosting. You can choose the OS that best suits your needs, whether it’s a Linux distribution like Ubuntu, CentOS, or Debian, or even a Windows Server operating system. This flexibility allows you to install and configure any software compatible with your chosen OS.
The isolation provided by the hypervisor is paramount. It ensures that what happens on one VPS doesn’t affect others on the same physical machine. If one VPS experiences a sudden traffic surge, crashes, or is compromised by malware, the other VPSs remain unaffected. This is because the hypervisor strictly enforces the resource boundaries and prevents virtual machines from interfering with each other.
The hypervisor presents virtualized hardware to the VPS. So, inside your VPS, everything looks and feels like a dedicated physical server. This is a key benefit and one of the ways it offers many advantages over a shared hosting environment.
Virtual Private Server Pros and Cons
Like any hosting solution, a Virtual Private Server (VPS) has its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these pros and cons is crucial for deciding if a VPS is the right choice for your needs. A VPS offers a middle ground between shared hosting and dedicated servers, balancing cost, performance, and control.
VPS Pros
The main advantages of a VPS stem from its dedicated resources and isolated environment.
- Improved Performance: Compared to shared hosting, a VPS offers significantly better performance. Your website or application will load faster and handle more traffic because you have dedicated CPU, RAM, and storage that aren’t shared with other users.
- Enhanced Security: A VPS provides a more secure environment than shared hosting. The isolation provided by the hypervisor means that security breaches on other VPSs on the same physical server won’t affect you.
- Greater Control and Customization: With root access (administrator-level access) to your VPS, you have complete control over the operating system and software. You can install any compatible software you need, customize server settings, and optimize performance for your specific applications.
- Scalability: Most VPS providers offer easy scalability. If you need more resources (e.g., more RAM or storage), you can often upgrade your plan without significant downtime or complex migrations. This is ideal for growing websites and businesses. For example, if you are launching a marketing campaign, you can prepare for a surge in traffic with a simple plan upgrade.
- Cost-Effectiveness: A VPS offers a good balance between cost and performance. It’s generally more expensive than shared hosting but significantly less expensive than a dedicated server, while providing many of the benefits of dedicated resources.
VPS Cons
While a VPS offers many advantages, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider.
- Higher Cost than Shared Hosting: While more affordable than dedicated servers, a VPS is still more expensive than shared hosting. This reflects the dedicated resources and increased performance you receive.
- Requires More Technical Knowledge (Especially Unmanaged): Managing a VPS, especially an unmanaged one, requires more technical expertise than managing a shared hosting account. You’ll be responsible for tasks like server configuration, software updates, and security hardening. If you choose a managed VPS, the hosting provider handles many of these tasks, but you’ll still need some basic technical understanding.
- Resource Limits (Though Dedicated): While your resources are dedicated, they are still limited by your chosen VPS plan. If your website or application consistently exceeds these limits, you’ll need to upgrade to a more powerful plan.
- Potential for Overselling (Less Common Now): In the past, some less reputable providers would oversell resources, meaning they’d allocate more resources to VPSs than the physical server could actually handle. This practice is less common with reputable providers today, thanks to improved virtualization technology and increased competition. Always choose a well-regarded VPS provider.
Comparing VPS to Other Web Hosting Types
Choosing the right web hosting type is crucial for your website’s success. A VPS is just one option, and it’s important to understand how it compares to other popular choices: shared hosting, dedicated servers, and cloud hosting. Each has its own set of trade-offs in terms of cost, performance, control, and complexity.
VPS vs. Shared Hosting
Shared hosting is the most basic and affordable type of web hosting. With shared hosting, your website shares a single server’s resources (CPU, RAM, storage) with many other websites. This is the entry point for most people.
- Key Difference: Resource allocation. Shared hosting means shared resources, while a VPS provides dedicated resources within a virtualized environment.
- Performance: A VPS offers significantly better performance than shared hosting. Your website will load faster and handle more traffic due to the dedicated resources.
- Security: A VPS is more secure because of its isolated environment. A security issue on one website in a shared hosting environment can potentially affect others.
- Control: A VPS provides much greater control with root access, allowing you to customize the server environment. Shared hosting offers very limited control.
- Cost: Shared hosting is cheaper than a VPS, reflecting its limitations.
- Best For: Shared hosting is suitable for small, low-traffic websites, personal blogs, or websites just starting out. A VPS is a better choice for growing websites, e-commerce stores, and applications that require more resources and control.
VPS vs. Dedicated Server
A dedicated server is a physical server dedicated entirely to a single user. You have exclusive access to all of the server’s resources.
- Key Difference: Physical vs. Virtual. A VPS is a virtual server running on shared hardware, while a dedicated server is a physical server dedicated solely to you.
- Performance: A dedicated server generally offers the highest level of performance, as you have full control over all hardware resources. However, a high-end VPS can often provide comparable performance for many applications.
- Control: Both offer full root access and control.
- Cost: Dedicated servers are significantly more expensive than VPSs, reflecting the cost of dedicated hardware.
- Scalability: VPSs are often easier to scale than dedicated servers. You can typically upgrade a VPS plan with minimal downtime. Scaling a dedicated server may require a more complex migration process.
- Best For: Dedicated servers are best for very high-traffic websites, large e-commerce platforms, resource-intensive applications, and businesses with strict security or compliance requirements. A VPS is a good step up from shared before the investment in Dedicated is required.
VPS vs. Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting is a broad term that encompasses various types of hosting services that utilize a network of virtual servers. It’s often confused with VPS hosting, but there are key distinctions. While a VPS is a type of cloud hosting, not all cloud hosting is a VPS.
- Key Difference: A traditional VPS is still tied to a single physical server (though virtualized). Cloud hosting, in its purest form, draws resources from a pool across many servers.
- Scalability: Cloud hosting is often touted for its superior scalability. Resources can be adjusted almost instantly, often automatically, based on demand. This is often referred to as “elasticity.” While VPSs can be scaled, it’s typically not as instantaneous.
- Pricing: Cloud hosting often uses a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where you only pay for the resources you actually consume. VPS plans typically have fixed monthly costs.
- Complexity: Cloud hosting can be more complex to manage than a traditional VPS, especially if you’re configuring a custom cloud infrastructure.
- Best For: Cloud hosting is ideal for applications with highly variable resource needs, applications that require high availability and redundancy, and large-scale projects. A traditional VPS is often a better fit for more predictable workloads and users who prefer a simpler, more traditional server environment. Cloud offers options and services that are much broader than the traditional VPS model.
When Should You Switch to a VPS Service?
You should switch to a VPS service when your website or application has outgrown the limitations of shared hosting, but you don’t yet need the full power (or expense) of a dedicated server. It’s a natural upgrade path.
Several key indicators suggest it’s time to consider a VPS. Recognizing these signs early can prevent performance issues and ensure a smooth user experience.
One of the most common signs is consistently slow website loading times. If your website is taking longer to load, even after optimizing images and code, it’s likely a resource issue. Shared hosting environments often struggle to handle traffic spikes or resource-intensive applications. A VPS, with its dedicated resources, can significantly improve loading times.
Another critical indicator is frequent downtime or errors. If you’re experiencing regular “500 Internal Server Errors” or other errors related to server resources, it’s a clear sign that your shared hosting plan can no longer cope. A VPS provides a more stable and reliable environment.
If you’re planning to run an e-commerce store, a VPS is almost always recommended. E-commerce sites require more resources to handle transactions, product catalogs, and customer data securely. The increased security and performance of a VPS are crucial for a successful online store.
Are you installing custom software or requiring specific server configurations? Shared hosting environments typically have strict limitations on what software you can install and how you can configure the server. A VPS, with its root access, gives you the freedom to customize the environment to your exact needs. For example, you might need to install a specific version of PHP, a custom database server, or a specialized caching system.
Increased website traffic is a positive sign of growth, but it also necessitates more server resources. If you’re seeing a steady increase in traffic, or if you’re anticipating a surge in traffic (e.g., due to a marketing campaign or product launch), upgrading to a VPS before you hit resource limits is a proactive step.
Finally, if security is a major concern, a VPS offers a more secure environment than shared hosting. The isolation between virtual servers minimizes the risk of your website being affected by security breaches on other websites hosted on the same physical server. This is particularly important for websites that handle sensitive user data.

Criteria for Choosing a Suitable VPS
Choosing the right VPS involves carefully considering several key factors. It is not a one-size-fits-all situation. The best VPS for you depends on your specific needs, technical skills, and budget. Prioritize these criteria to make an informed decision.
Resource Requirements (CPU, RAM, Storage, Bandwidth)
Start by assessing your website or application’s resource needs. This is the foundation of your decision. Consider your current traffic levels, anticipated growth, and the type of content you’ll be hosting.
- CPU: The number of CPU cores determines processing power. More cores are generally better for resource-intensive applications.
- RAM: RAM (Random Access Memory) is crucial for fast performance. Insufficient RAM can lead to slowdowns and even crashes.
- Storage: Consider the amount of disk space you need for your website files, databases, and operating system. SSD (Solid State Drive) storage offers significantly better performance than traditional HDD (Hard Disk Drive) storage.
- Bandwidth: Bandwidth determines the amount of data that can be transferred between your server and visitors. Choose a plan with enough bandwidth to handle your expected traffic.
Operating System (OS)
The choice of operating system (OS) depends on your technical preferences and the software you plan to use.
- Linux: Popular Linux distributions like Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian are common choices for VPS hosting. They are known for their stability, security, and flexibility.
- Windows Server: If you need to run applications that require a Windows environment (e.g., ASP.NET, Microsoft SQL Server), you’ll need a Windows VPS.
Managed vs. Unmanaged
This is a crucial decision that impacts your workload and responsibilities.
- Managed VPS: The hosting provider handles server maintenance, security updates, and software installations. This is ideal for users with limited technical expertise or those who prefer to focus on their website or application rather than server administration.
- Unmanaged VPS: You are responsible for all aspects of server management. This offers greater control and flexibility but requires significant technical knowledge.
Price
VPS pricing varies widely based on resources, managed/unmanaged status, and the provider. Compare plans carefully and consider the long-term costs. Don’t just choose the cheapest option; prioritize value and reliability.
Provider Reputation and Reliability
Choose a reputable VPS provider with a proven track record of reliability and good customer support. Read reviews, check uptime guarantees, and look for providers with a strong reputation in the industry.
Support
Consider the level of customer support offered by the provider. 24/7 support via live chat, phone, or email is essential, especially if you’re new to VPS hosting. Check the provider’s documentation and knowledge base.
Scalability
Choose a provider that allows you to easily scale your VPS resources up or down as your needs change. This ensures that you can adapt to traffic fluctuations and future growth without complex migrations.
Location
The physical location of the server can impact website loading times for your target audience. Choose a server location that is geographically close to your primary audience for optimal performance. Many providers offer multiple data center locations.
Backup
Ensure that the provider offers regular backups of your VPS. This is crucial for disaster recovery in case of data loss. Understand the backup frequency, retention policy, and restoration process.
VPS FAQs
This section addresses some frequently asked questions about Virtual Private Servers (VPSs) to provide a clearer understanding of this hosting option.
What is the difference between a VPS and a VPN?
A VPS (Virtual Private Server) and a VPN (Virtual Private Network) are completely different technologies, although their acronyms are similar. A VPS is a type of web hosting, while a VPN is a tool for online privacy and security that encrypts your internet connection.
Is VPS hosting secure?
Yes, VPS hosting is generally considered more secure than shared hosting. The key reason is the isolation between virtual servers. If one VPS on a physical server is compromised, it’s unlikely to affect other VPSs. However, security also depends on proper server configuration and maintenance.
Can I host multiple websites on a single VPS?
Yes, you can typically host multiple websites on a single VPS, provided you have sufficient resources (CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth). The number of websites you can host depends on the size and resource requirements of each website. Using a control panel like cPanel or Plesk can simplify managing multiple websites.
What is the difference between managed and unmanaged VPS?
The key difference lies in who is responsible for server management. With a managed VPS, the hosting provider handles tasks like operating system updates, security patches, and software installations. With an unmanaged VPS, you are responsible for all of these tasks.
Do I need a VPS for my website?
Whether you need a VPS depends on your website’s size, traffic, resource requirements, and your technical expertise. If you’re experiencing performance issues with shared hosting, need more control, or anticipate growth, a VPS is likely a good option.
What operating system can I use on a VPS?
You can typically choose from a variety of Linux distributions (like Ubuntu, CentOS, Debian) and Windows Server versions. The best choice depends on your specific needs and technical preferences. Most providers will offer multiple options for you to choose from.
How much does a VPS cost?
VPS pricing varies widely depending on the provider, resources (CPU, RAM, storage, bandwidth), and whether it’s managed or unmanaged. Prices can range from a few dollars per month for basic, unmanaged VPSs to hundreds of dollars per month for high-end, managed VPSs.
How do I choose a VPS provider?
Consider factors like reputation, performance, support, pricing, features, and the specific needs of your website or application. Look for providers with good reviews, reliable uptime, and responsive customer support. Read reviews and compare plans carefully before making a decision. Consider what is important to you.
What is Root Access?
Root access is having administrator-level privileges and control over the entire operating system on a VPS server. This enables users to install, configure, and modify any software, as well as customize server settings to meet specific requirements.
