Ever saved a photo on your phone, written a document on your computer, or downloaded a song? If so, you’ve used file storage! It might sound technical, but it’s simply the way we keep all our digital information safe and organized.
If you’ve ever wondered “What is file storage, really?”, you’re in the right place. This guide will break it down in plain English, with simple examples you already know. We’ll explore what it is, why it’s crucial, and where you use it every single day.
So, What Exactly Is File Storage? The Basic Definition
File storage is the method computers and digital devices use to save and retrieve digital information. Think of things like your documents, photos, videos, music, and software applications. It’s the fundamental way digital ‘stuff’ is kept for later use.
Imagine a physical filing cabinet in an office. You put important papers (files) into folders, and then place those folders neatly into the cabinet drawers (storage). File storage works on a similar principle, but for your digital world. It provides a structured place to keep everything organized.
Instead of paper, you have digital files. These can be text documents you write, pictures you take, songs you listen to, or even the apps you use. File storage is the container holding all these digital items.
The core purpose is persistence. This means the information stays saved even when you turn off your device. Without file storage, everything would disappear the moment the power went out. It ensures your data endures over time.
This digital “container” isn’t just one thing. It can be a physical part inside your computer, a small device you plug in, or even vast online systems. We’ll look at these different types soon. The key idea is having a dedicated place for your files.
Understanding file storage helps you manage your digital life better. Knowing where your files are and how they are saved is essential in today’s technology-driven world. It empowers you to organize, protect, and access your valuable information effectively.
Why Do We Need File Storage?
We need file storage primarily to save our digital work, memories, and information so we can access it later. It’s the foundation for keeping any data long-term on digital devices. Without it, computers and smartphones couldn’t perform their most basic functions.
The most obvious reason is saving your creations. Whether it’s a report for school, a presentation for work, or a digital painting, file storage lets you keep it. You can close the file and open it again tomorrow, continuing where you left off.
It’s also crucial for storing memories. Digital photos and videos capture important moments. File storage provides the space to keep these irreplaceable memories safe, allowing you to revisit them whenever you wish. Think of it as your digital photo album or video library.
Furthermore, file storage is essential for software to work. Operating systems (like Windows, macOS, or Android) need to be stored somewhere. The applications you install, from web browsers to games, also reside in file storage. They are loaded from storage into memory when you run them.
Organization is another key benefit. File storage systems allow you to create folders (also called directories) to group related files. This makes finding specific information much easier, just like organizing papers in a physical filing cabinet. Good organization saves time and reduces frustration.
Consider the sheer amount of digital information generated daily. Globally, humans create quintillions of bytes of data every single day! File storage technologies are constantly evolving to handle this massive scale, providing the capacity needed for personal use, businesses, and scientific research.
Without reliable file storage, the digital world as we know it couldn’t exist. Banking, communication, entertainment, education – nearly every aspect of modern life relies heavily on the ability to store and retrieve digital information accurately and efficiently.
Where Do You Find File Storage?
You find file storage everywhere in digital life, from the device in your pocket to vast online systems. It’s not a single, abstract concept but takes many physical and virtual forms that you likely interact with daily without even realizing it.
Think about the devices you use regularly. Your smartphone, your laptop, your tablet, even smart TVs and gaming consoles – they all contain some form of file storage. It’s built-in, allowing them to hold apps, photos, and user settings.
Let’s explore the most common places you’ll encounter file storage: inside your devices, on portable gadgets you carry, and increasingly, in the ‘cloud’ online. Understanding these helps you see how central file storage is.
Inside Your Computer or Laptop (Local Storage)
Your computer’s main file storage is usually an internal hard drive (HDD) or a solid-state drive (SSD). This is often called local storage because the storage medium is physically located inside the device you are using.
An HDD (Hard Disk Drive) is a traditional type of storage. It uses spinning magnetic disks (platters) to store data. Think of it like a tiny record player, with read/write heads moving across the spinning disks. HDDs typically offer large storage capacities at a lower cost.
An SSD (Solid-State Drive) is a newer, faster type of storage. It uses flash memory chips, similar to those in USB drives or smartphones, with no moving parts. This makes SSDs much faster, more durable, and quieter than HDDs, though often more expensive for the same capacity.
This internal storage holds your computer’s Operating System (OS) – the core software like Windows, macOS, or Linux that manages everything. It also stores your installed applications, programs, games, and the personal files you save directly onto the computer.
When you save a document or download a picture directly to your computer’s “Documents” or “Pictures” folder, you are using its local file storage. It’s readily accessible whenever you use that specific computer.
The capacity of this local storage is measured in bytes. You’ll commonly see terms like Gigabytes (GB) or Terabytes (TB). One TB is roughly 1000 GB. This capacity determines how many files, applications, and media you can store directly on the device.
On External Devices (Portable Storage)
Portable file storage includes devices like USB flash drives or external hard drives that you plug into your computer. These offer a convenient way to move files around or add extra storage space without opening up your computer.
USB flash drives (also known as thumb drives or memory sticks) are small, inexpensive, and highly portable. They use flash memory chips like SSDs. People often use them to quickly transfer documents, presentations, or photos between computers. Their capacity ranges from a few GB to over a TB.
External hard drives are larger storage devices that connect to your computer, usually via a USB cable. They can contain either an HDD or an SSD inside their casing. They offer much larger capacities than typical USB flash drives, making them ideal for backing up your entire computer or storing large media libraries (like movies or extensive photo collections).
Portable storage is great for backups. A backup is a copy of your important files kept separately. If something happens to your computer’s internal drive (like failure or damage), having a backup on an external device can save your data.
These devices provide physical control over your data. You can connect them when needed and disconnect them for safekeeping. They don’t require an internet connection to access the files stored on them, unlike cloud storage.
In the Cloud (Online/Remote Storage)
Cloud file storage means saving your files online, on servers managed by companies like Google, Apple, or Dropbox. When you use cloud storage, your files aren’t stored directly on your own device but on powerful computers (servers) located in data centers, potentially thousands of miles away.
The “Cloud” isn’t a fluffy white thing in the sky; it’s just a term for this network of remote servers accessed via the internet. This is also known as remote storage because the storage is not local to your device.
Popular examples of cloud storage services include Google Drive, Apple iCloud, Microsoft OneDrive, and Dropbox. Many offer a certain amount of free storage and options to pay for more capacity. You typically access your files through a website or a dedicated app.
One major benefit is accessibility. You can usually access your cloud files from any device (computer, phone, tablet) that has an internet connection. This makes it easy to work on a document at home and continue editing it at the office or on the go.
Collaboration is another advantage. Cloud storage services often make it simple to share files or entire folders with friends, family, or colleagues. Multiple people can even work on the same document simultaneously in some cases.
Cloud storage also often serves as a form of backup. Files stored in the cloud are generally safe from issues affecting your local device, like hardware failure, theft, or damage. The service provider manages the underlying hardware and data redundancy.
However, you need an active internet connection to access most cloud files. Also, control over the data resides with the service provider, which raises privacy and security considerations for some users.
How Does File Storage Keep Things Organized? (A Quick Peek)
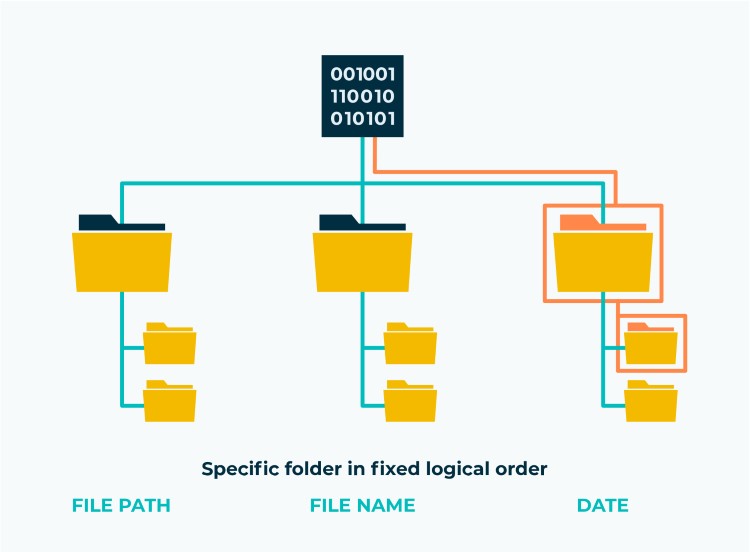
File storage uses a system, called a ‘file system’, to organize data into files and folders you can navigate. It acts like a librarian or an office manager for your digital data, imposing rules and structure so that information can be stored, found, and retrieved efficiently.
Think of a huge, empty warehouse (your storage drive). A file system is the set of rules and structures (like adding shelves, labels, and an inventory list) that turns that empty space into a usable storage area. It defines how files are named, stored, and organized.
When you format a storage drive (like a new hard drive or USB stick), you are essentially applying a file system to it. Common file systems include NTFS (used by Windows), APFS or HFS+ (used by macOS), and ext4 (used by Linux). You usually don’t need to worry about these technical names, as the OS handles them.
The most visible part of the file system for users is the ability to create folders (also called directories). These allow you to group related files together. You can create folders within folders, creating a hierarchical structure (like branches on a tree) to keep things tidy.
The file system keeps track of crucial information about each file, known as metadata. This includes the file’s name, its size, the date it was created or modified, and, importantly, exactly where on the physical storage medium (like the spinning disk of an HDD or the chips of an SSD) the file’s data is located.
So, when you double-click a file icon, the operating system uses the file system’s “inventory list” (its internal tables) to quickly find all the pieces of that file on the drive and present them to you as a single, coherent item.
Without a file system, a storage drive would just be a jumbled collection of data bits with no way to distinguish one file from another or locate specific information. It provides the essential organization needed for file storage to be useful.
File Storage: Your Digital Filing Cabinet
In summary, file storage is the essential digital ‘space’ where all your files live, organized and ready for use. It’s the fundamental technology allowing computers, phones, and countless other devices to save and retrieve digital information persistently.
We’ve seen it’s like a digital filing cabinet, keeping everything from important documents and precious photos to the software that makes our devices work. Its primary importance lies in preserving data so we can access it whenever needed.
You encounter file storage in many forms:
- Local storage: Inside your computer (HDDs, SSDs).
- Portable storage: Devices you carry (USB drives, external HDDs).
- Cloud storage: Online services (Google Drive, iCloud, Dropbox).
Behind the scenes, a file system provides the necessary organization, managing files and folders, and tracking where everything is located on the storage medium. This allows you easily navigate and access your digital world.
Understanding the basics of file storage empowers you. You can make better decisions about where to save your files, how to organize them, and how to ensure your important digital information is kept safe. It’s a core concept of modern computing, and now you know what it’s all about!
For projects needing reliable, high-performance storage beyond everyday files, consider a powerful option. Vietnam VPS utilizes new-gen dedicated hardware like AMD EPYC Gen 3 processors and NVMe U.2 SSDs, delivering high speed, stability, and optimized capacity affordably, ensuring quality performance for your demanding applications.
