In the world of virtualization, Hypervisor Type 2 (also known as hosted hypervisor) plays an essential role, particularly for individuals and smaller organizations that want to run virtual machines (VMs) without complex infrastructure. While Hypervisor Type 1 runs directly on hardware, Type 2 operates within an existing host operating system.
This subtle difference significantly impacts the way Type 2 hypervisors work, their performance, and their ideal use cases. In this blog, we’ll explore what Hypervisor Type 2 is, its key features, benefits, and where it fits best in today’s technology landscape.
What is a Hypervisor Type 2 (Hosted Hypervisor)?
A Hypervisor Type 2 is a virtualization platform that runs on top of an existing operating system. Unlike Type 1 hypervisors, which install directly on physical hardware, Type 2 hypervisors depend on the host OS to function. Essentially, they are applications that run on a regular operating system, and they rely on the host OS for managing hardware resources such as CPU, memory, and storage.
This architecture is simpler and more user-friendly, which is why it is commonly used for personal virtualization, development environments, and testing purposes. Examples of Type 2 hypervisors include VMware Workstation, Oracle VirtualBox, Parallels Desktop, and Hyper-V for Windows.
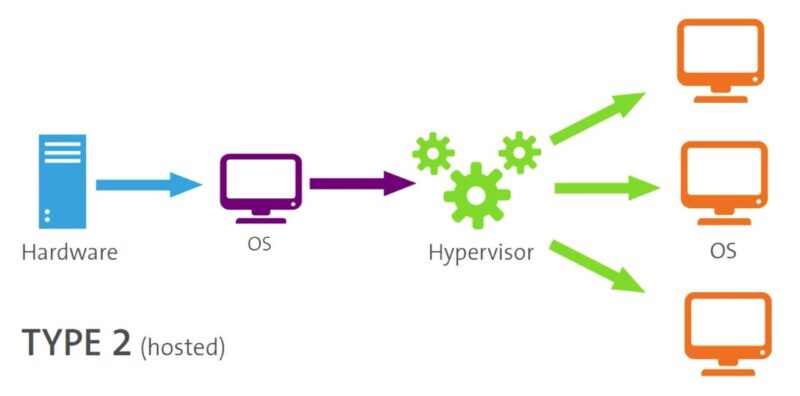
How Does Hypervisor Type 2 Work?
A Type 2 hypervisor works by utilizing the resources of the host operating system. Once installed as an application on the host OS, the hypervisor creates virtual machines (VMs), each of which behaves like a separate physical computer. The virtual machines can run their own operating systems (such as Windows, Linux, macOS, etc.), independent of the host operating system.
The hypervisor allocates resources to the VMs based on what is available from the host system. The host operating system provides memory, processing power, and storage to the virtual machines, but it also controls access to the hardware, making Type 2 hypervisors dependent on the efficiency of the host OS.
Key Features of Hypervisor Type 2
- Dependence on Host OS: Unlike Type 1 hypervisors that work directly with hardware, Type 2 hypervisors rely on the host OS to manage the hardware. This creates a layered virtualization approach, where the host OS acts as a middleman between the hypervisor and physical resources.
- Ease of Installation and Setup: One of the primary advantages of Type 2 hypervisors is their ease of installation. They can be quickly installed as applications on a wide range of host operating systems. This makes them highly accessible for individuals and organizations with limited IT infrastructure.
- Resource Sharing: Type 2 hypervisors use the resources of the host system, which means the performance of the virtual machines can be limited by the efficiency and available resources of the host OS. This can cause a slight performance drop compared to Type 1 hypervisors, which operate directly on hardware.
- Multiple OS Support: Type 2 hypervisors allow you to run multiple operating systems on the same physical machine, making them ideal for testing, development, and running software on different platforms. For example, you can run a Windows VM on a macOS system or vice versa.
Benefits of Hypervisor Type 2
Simpler Setup and Use
One of the biggest advantages of Type 2 hypervisors is their simplicity. They do not require complex hardware configurations, and the setup process is user-friendly, making them perfect for developers, testers, and home users.
Ideal for Desktop Virtualization
Type 2 hypervisors are well-suited for personal or small-scale desktop virtualization. If you need to run a different OS or test applications in a controlled environment, Type 2 hypervisors are an easy and efficient way to do so without altering your physical machine.
Cost-Effective
Since Type 2 hypervisors use the existing host OS and don’t require dedicated hardware, they are typically more cost-effective than Type 1 hypervisors. This makes them a good option for personal use, small businesses, or development environments.
Support for Multiple Guest OS
Just like Type 1, Type 2 hypervisors can host multiple VMs with different operating systems. This versatility allows you to run different environments, which is especially useful for software development, testing, and learning purposes.
Drawbacks of Hypervisor Type 2
Lower Performance
The primary drawback of Type 2 hypervisors is their reliance on the host OS. Since the host OS is responsible for managing hardware, this introduces additional overhead. This can result in lower performance for virtual machines compared to Type 1 hypervisors, which have direct access to the hardware.
Limited Scalability
While Type 2 hypervisors work well for small-scale environments, they are not designed to handle the massive scale that Type 1 hypervisors can manage. Running multiple VMs on a single physical server can be taxing on the host OS, especially if you’re dealing with resource-heavy applications.
Security Risks
Since Type 2 hypervisors rely on the host OS, any vulnerabilities in the host OS can potentially affect the virtual machines running on the hypervisor. Additionally, the added layer of software means there is more potential for security breaches.
Popular Hypervisor Type 2 Examples
- VMware Workstation: One of the most popular Type 2 hypervisors, VMware Workstation is used for running multiple operating systems on a desktop or laptop. It is widely used by developers for software testing and by IT professionals for creating virtualized test environments.
- Oracle VirtualBox: A free and open-source Type 2 hypervisor that supports a wide range of host and guest operating systems. It’s an excellent choice for those looking for a cost-effective solution for running VMs on their desktop or laptop.
- Parallels Desktop: This Type 2 hypervisor is specifically designed for Mac users who want to run Windows and other operating systems on their Macs. Parallels is known for its seamless integration between macOS and Windows.
- Hyper-V for Windows: Microsoft’s Type 2 hypervisor is included with Windows 10 Pro and Enterprise editions. It allows users to run multiple VMs on a Windows machine, making it ideal for developers and IT professionals working in Windows environments.
Ideal Use Cases for Hypervisor Type 2
- Development and Testing: Type 2 hypervisors are perfect for developers who need to test software across different operating systems. You can run multiple OS environments (e.g., Windows, Linux, macOS) on a single machine without the need for separate physical systems.
- Personal Virtualization: If you’re an enthusiast or hobbyist who wants to experiment with different operating systems, Type 2 hypervisors provide a low-cost solution. For example, running Linux on a Windows PC or running a virtualized version of macOS on a Windows machine.
- Learning and Education: For those learning about different operating systems, networking, or cybersecurity, Type 2 hypervisors provide an easy way to set up virtual labs. Students can test various OS configurations and network setups without needing multiple physical machines.
- Running Legacy Applications: If you need to run older applications that require outdated operating systems, Type 2 hypervisors are a great solution. You can install a VM with an older OS, preserving compatibility without affecting the primary machine’s environment.
In summary, Hypervisor Type 2 provides a convenient and cost-effective solution for running virtual machines on personal systems, development environments, and small-scale virtualized infrastructures. While Type 2 hypervisors may not offer the same level of performance, scalability, and security as Type 1 hypervisors, they are ideal for users who need to run multiple operating systems for testing, development, or personal use.
With their ease of setup and flexibility, Type 2 hypervisors are a go-to choice for desktop virtualization and experimentation with different OS environments. Whether you’re a developer, student, or tech enthusiast, a Type 2 hypervisor can provide a powerful tool for running virtualized systems on a single machine.
